Introduction
When diving into the world of Amazon Web Services (AWS), one concept that stands out as crucial yet often misunderstood is the AWS Shared Responsibility Model. Whether you’re a newbie or a seasoned pro, understanding this model is fundamental to securing your data and applications in the cloud. So, let’s break it down, shall we?
Understanding the AWS Shared Responsibility Model
Definition and Overview
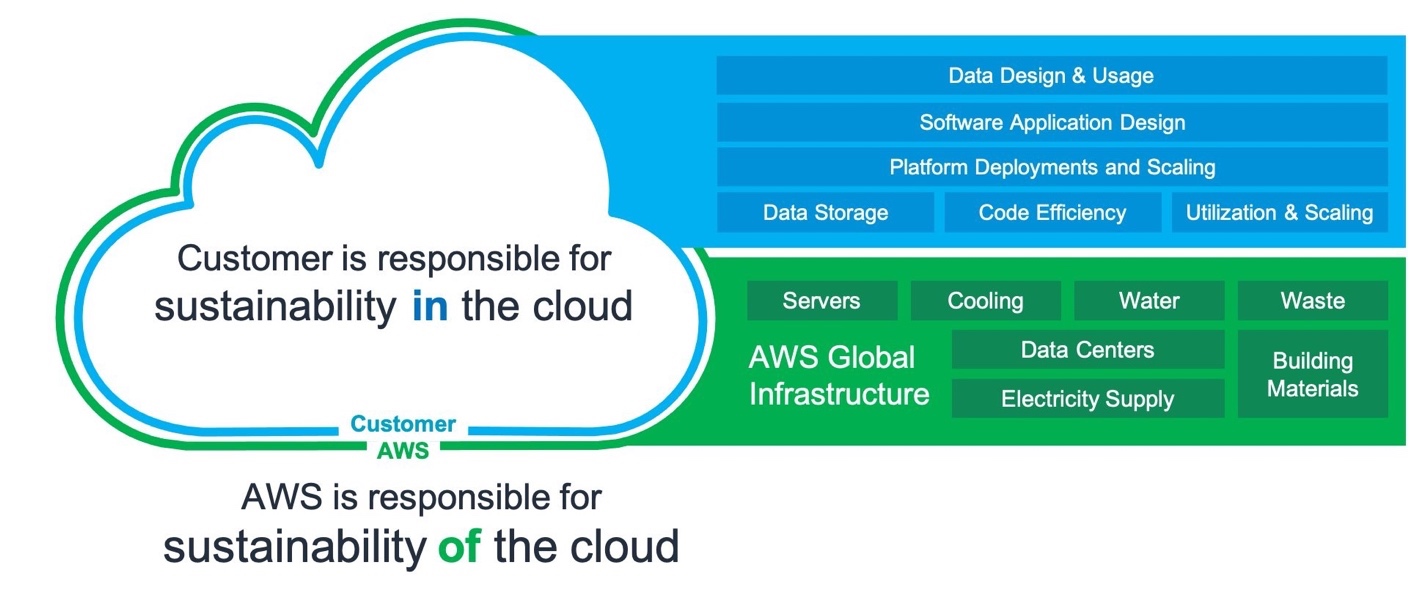
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model is essentially a security framework that outlines the responsibilities of both AWS and its customers. This clear delineation ensures that both parties know their roles in maintaining a secure cloud environment.
Customer Responsibilities
As a customer, you’re responsible for securing and managing the data you put in the cloud, including:
- Data Protection: Encrypting data at rest and in transit.
- Identity and Access Management: Controlling user access through IAM policies.
- Operating System and Network Configuration: Keeping your operating systems and networks secure and updated.
- Application Security: Ensuring your applications are developed and maintained securely.
AWS Responsibilities
AWS, on the other hand, takes care of the security of the cloud, including:
- Physical Security: Protecting data centers.
- Infrastructure Maintenance: Keeping the hardware and software up to date.
- Managed Services Security: Securing managed services like RDS, Lambda, etc.
- Compliance and Assurance: Ensuring the infrastructure meets various compliance standards.
Security in the Cloud vs. Security of the Cloud
Explanation of Security in the Cloud
Security in the cloud refers to the security measures that customers must implement to protect their data and applications within the cloud environment.
Explanation of Security of the Cloud
Security of the cloud refers to AWS’s responsibility to protect the infrastructure that runs all the services offered in the AWS Cloud.
Customer Responsibilities
Data Protection
Keeping your data safe is paramount. Encrypt your data both at rest and in transit to shield it from unauthorized access.
Identity and Access Management
IAM is crucial. Use AWS IAM to manage user access and permissions effectively, ensuring that only authorized users have access to your resources.
Operating System and Network Configuration
Regularly update and patch your operating systems and configure your networks securely to defend against vulnerabilities.
Application Security
Develop and maintain your applications with security in mind, regularly testing for vulnerabilities and applying patches as needed.
AWS Responsibilities
Physical Security
AWS takes significant measures to ensure physical security, including restricting access to data centers and monitoring them continuously.
Infrastructure Maintenance
AWS handles the maintenance of the underlying infrastructure, ensuring it is secure and up to date with the latest patches and updates.
Managed Services Security
When you use AWS managed services, AWS ensures that these services are secure and compliant with industry standards.
Compliance and Assurance
AWS provides compliance programs and assurance mechanisms to help you meet your regulatory and compliance requirements.
Shared Controls
Patch Management
Both AWS and customers share the responsibility for patch management. AWS manages the infrastructure patches, while customers handle patches for their operating systems and applications.
Configuration Management
AWS provides tools and services to help you manage your configurations, but it’s your job to use these tools to keep your environment secure.
Awareness and Training
While AWS offers a variety of resources and training, it’s up to you to ensure your team is well-trained and aware of security best practices.
Data Security
Encryption Best Practices
Encrypting your data is essential. Use AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to manage your encryption keys and ensure your data is protected.
Backup and Recovery Strategies
Implement robust backup and recovery strategies to protect against data loss. Regularly test your backups to ensure they can be restored when needed.
Data Integrity
Ensure the integrity of your data by using checksums and data validation methods. AWS provides tools like Amazon S3 and DynamoDB to help maintain data integrity.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Importance of IAM
IAM is vital for controlling who can access your AWS resources. Proper IAM policies can prevent unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Best Practices for IAM
Follow best practices such as using multi-factor authentication (MFA), regularly rotating credentials, and granting the least privilege necessary.
IAM Tools Provided by AWS
AWS offers several IAM tools, including IAM roles, policies, and identity federation, to help you manage access securely and efficiently.
Operational Security
Monitoring and Logging
Use AWS CloudTrail and Amazon CloudWatch to monitor your AWS environment and log all activities. This helps in detecting and responding to security incidents promptly.
Incident Response Planning
Have a solid incident response plan in place. Regularly test and update it to ensure you can quickly respond to any security incidents.
Regular Audits
Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in your environment.
Application Security
Secure Development Practices
Develop applications with security in mind from the outset. Follow secure coding practices and conduct regular code reviews.
Testing and Vulnerability Management
Regularly test your applications for vulnerabilities using tools like AWS Inspector and apply patches promptly.
Third-Party Application Considerations
When using third-party applications, ensure they meet your security standards and are regularly updated to address new vulnerabilities.
Network Security
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Create isolated networks using AWS VPC to enhance security. Control traffic flow with security groups and network ACLs.
Security Groups and Network ACLs
Use security groups and network ACLs to control inbound and outbound traffic to your instances, ensuring only authorized traffic is allowed.
DDoS Protection
Protect against DDoS attacks using AWS Shield and AWS WAF. These services help safeguard your applications and data from malicious traffic.
Compliance and Assurance
AWS Compliance Programs
AWS offers a range of compliance programs that meet various regulatory requirements, helping you maintain compliance in your cloud environment.
Customer Compliance Responsibilities
While AWS provides a compliant infrastructure, it’s your responsibility to ensure your applications and data meet regulatory requirements.
Auditing and Reporting
Use AWS tools to conduct audits and generate compliance reports, ensuring your environment adheres to required standards.
Best Practices for Customers
Regular Security Reviews
Conduct regular security reviews to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Stay proactive in maintaining a secure environment.
Staying Informed on AWS Updates
Keep abreast of AWS updates and new features. AWS frequently releases new services and security enhancements that can benefit your environment.
Leveraging AWS Security Services
Make the most of AWS security services like AWS Config, AWS GuardDuty, and AWS Security Hub to enhance your security posture.
Common Misconceptions
Misunderstanding the Model
Many believe AWS handles all security, but it’s a shared model. Understanding your responsibilities is crucial.
Over-reliance on AWS Security
Relying solely on AWS for security can lead to vulnerabilities. It’s essential to actively manage your security responsibilities.
Ignoring Customer Responsibilities
Failing to secure your applications and data can result in breaches. Always prioritize your security responsibilities.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, the AWS Shared Responsibility Model is about partnership. AWS provides a secure infrastructure, but you must secure your data and applications within that infrastructure. By understanding and embracing your responsibilities, you can ensure a robust and secure cloud environment.
FAQs
What is the AWS Shared Responsibility Model? The AWS Shared Responsibility Model is a framework that delineates the security responsibilities between AWS and its customers, ensuring a secure cloud environment.
How does AWS ensure physical security? AWS ensures physical security through restricted access to data centers, continuous monitoring, and stringent security measures to protect the infrastructure.
What are the main customer responsibilities in the AWS Shared Responsibility Model? Customers are responsible for data protection, identity and access management, operating system and network configuration, and application security.
Why is data encryption important in AWS? Data encryption is crucial because it protects your data from unauthorized access, ensuring its confidentiality and integrity both at rest and in transit.
How can customers stay compliant with AWS standards? Customers can stay compliant by following AWS’s best practices, leveraging AWS compliance programs, and regularly conducting security audits and assessments.